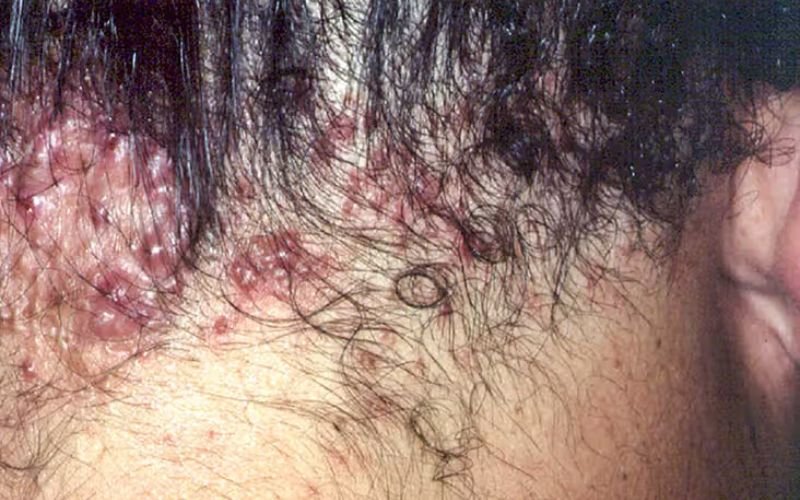
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) represents a persistent inflammatory condition that affects neck tissue together with skin at the back of the head. This dermatological problem is described by the advancement of firm, raised papules and keloid-like knobs, frequently bringing about scarring and balding. AKN is also known as folliculitis keloidalis or dermatitis papillaris capillitia. AKN presents both physical and mental difficulties for those impacted, affecting their satisfaction. The article published in Wiley Online Library reported AKN to be a chronic inflammation that causes trauma to hair follicles and suggests various topicals, antibiotics, and intralesional steroid injections can be used for its treatment. This article discusses the reasons, symptoms, and dermatologist-approved treatment methods for acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) which affects the skin of the scalp persistently.
AKN causes and risk factors
The specific reason for the occurrence of acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) remains elusive, yet a few elements are expected to aggravate it. The condition is generally connected with ongoing irritation of the hair follicles in the impacted region. Normal causes and risk factors include:
- Haircutting practices: A regular reason for AKN is the nearby shaving or trimming of hair in the impacted area. This repetitive injury to the hair follicles can set off a provocative reaction.
- Curly hair: People with firmly twisted or unusual hair are more inclined toward creating AKN. The wavy idea of hair might add to ingrown hairs, prompting aggravation and ensuing keloid development.
- Friction and irritation: Contact brought about by close collars, clothing, or increased perspiration in the neck locale might add to the turn of events or worsening of AKN.
- Bacterial and fungal infections: Contaminations, especially bacterial and parasitic, can assume a part in the AKN. Poor cleanliness practices might add to the progression of these diseases.
Symptoms
The side effects of this disease include the presence of papules, pustules, and keloid-like knobs in the impacted region.
Papules and pustules
Little, firm papules looking like acne sores frequently show up in the beginning phases. Pustules may likewise be present, showing inflammation and irritation.
Keloid-like nodules
After some time, the papules might advance to frame bigger, raised knobs with an inclination to keloid development. These knobs can be irritated and agonizing.
Scarring and hair loss
Constant AKN can prompt scarring hair thinning and loss in the impacted area. The scarring might be deforming and affect the individual’s confidence.
Diagnosis
For an appropriate diagnosis of acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN), doctors need to physically examine patients while understanding their entire medical history. Doctors conduct border examinations of affected skin areas before conducting optional tests such as skin biopsy analysis to confirm their diagnosis. Patients with AKN need correct diagnosis since their symptoms can mimic those seen in pseudofolliculitis barbae or dissecting cellulitis.
Dermatologist-recommended AKN solutions
Multiple treatment approaches are essential to reduce inflammation and stop scarring in acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN). AKN treatment choices might include:
Topical steroids
Effective steroids are generally endorsed to diminish inflammation and lighten side effects. They can be viable in the beginning phases of AKN.
Oral antibiotics
Antitoxins, like antibiotic medication or doxycycline, might be endorsed to battle bacterial contamination and aggravation. These meds are much of the time utilized related to skin medicines.
Topical retinoids
Retinoids, derived from vitamin A, can assist with normalizing follicular epithelial desquamation and diminish the risk of additional irritation. They are in many cases utilized in the treatment of AKN.
Intralesional corticosteroid injections
Corticosteroids deliver direct injections into large stiff nodules to provide pain relief and combat the disease.
Laser therapy
The medical procedure uses both pulsed dye laser and ablative laser for treating scars while encouraging collagen development. This can be especially gainful in situations where keloid development has happened.
The article published in the National Library of Medicine has reported the treatment of AKN with 1064nm neodymium garnet laser, 810-nm diode laser, and CO2 laser has proved to cause 82–95% improvement in AKN condition within 1–5 sessions.
Surgical intervention
In serious cases, careful extraction of bigger keloid-like knobs might be considered. Nonetheless, careful methodologies are frequently saved for cases impervious to different medicines because of the risk of regrowth and scarring.
Preventive measures
Providing people with important prevention knowledge stands as the essential step. Patients should refrain from shaving near affected areas while maintaining proper hygiene and reducing the potential for irritation.
Prognosis and complications
The prognosis for skin inflammation keloidalis nuchae differs, and successful administration frequently requires progressive care and consideration regarding preventive measures. While certain people might overcome the side effects with proper treatment, others may encounter reoccurrence or tenacious injuries.
Entanglements of AKN can incorporate scarring, hyperpigmentation, and extremely permanent balding in the impacted region. The mental effect of the condition ought to be considered carefully, as people with AKN might encounter shame, hesitance, or decreased personal satisfaction.
Prevention strategies
Proper prevention of acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) involves implementing specific techniques that minimize harm to hair follicles and hair strands. Key preventive strategies include.
- Gentle hair care practices: Try not to close shave and pick longer haircuts that reduce friction and injury to the scruff of the neck.
- Avoidance of irritants: Established synthetic chemicals present in particular haircare products have the potential to enhance skin sensitivity. Choosing soft and low-allergic products helps minimize the problem.
- Proper haircutting techniques: Sharp trimmer use combined with limited haircut frequency will help minimize injuries.
- Avoidance of tight hairstyles: Wearing tight hairstyles at the shaft of the hair leads to increased irritation. Loose haircuts can assist with limiting this disease.
- Prompt treatment of ingrown hairs: Tending to ingrown hairs quickly can forestall the occurrence of incendiary sores.
Lifestyle and home care
Notwithstanding clinical concerns, people with AKN can embrace specific practical dietary changes, lifestyle maintenance and home care routine practices to deal with their condition.
- Gentle hair care: The use of delicate hair care techniques which include avoiding tight hairstyles along with reduced washing friction helps stop additional damage to the hair.
- Avoidance of trauma: The risk to hair follicles becomes severe when individuals expose the affected area with extreme hair trimming or facial shaving.
- Good hygiene: Regular hygienic cleaning of infected areas works to block simultaneous infections from bacteria and parasites.
- Avoidance of irritants: The inflammatory symptoms of patients become more manageable when they avoid activities that cause inflammation such as wearing tight neckwear.
Maintenance therapy for AKN
Acne keloidalis nuchae functions as a chronic skin disease that demands complex customized therapeutic strategies for treatment. AKN patients can experience a better quality of life by receiving treatment alongside implementing life changes and home remedies. Patients need immediate treatment together with early intervention to stop the condition from worsening and avoid long-lasting bald patches and scars. People encountering initial symptoms of AKN ought to look for brief clinical consideration from a certified dermatologist for an exact diagnosis and appropriate management plan.
“Take control of Acne Keloidalis Nuchae today! To safeguard your hair and skin, see a dermatologist for early treatment and preventive care.”